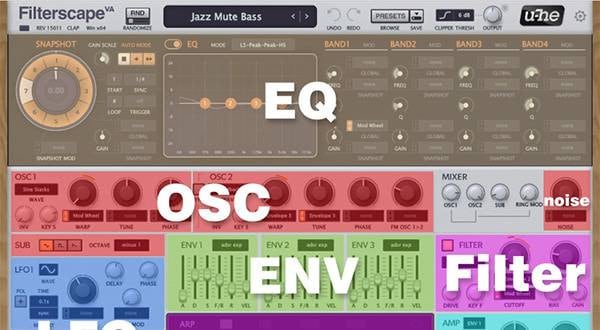
Filterscape VA has a standard analog synth configuration, which is unusual for u-he company. This article mainly deals with common parts of analog synths, so the contents can be applied to other synths as well.
What is FILTER?
In general analog synthesizers and subtractive synthesizers, the filter is the key to tone creation. The sawtooth wave output from an oscillator, for example, contains many overtones, which can be filtered out to create the desired sound. Filter generally means “filtration”. In the case of sound, it means determining the bandwidths to pass through and the bandwidths to block. In synths, low-pass filters that only allow low-frequency components to pass through, are the most common. Other types of filters include high-pass filters that pass only high-frequency components, band-pass filters that pass only certain bandwidths, and notch filters that, conversely, block certain bandwidths.
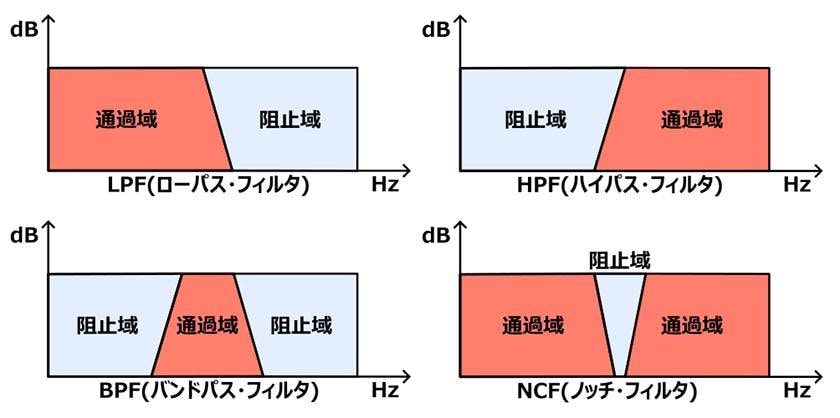
The video below shows the changes that occur when a sawtooth wave is subjected to LPF. You can see that the overtone component is gradually removed.
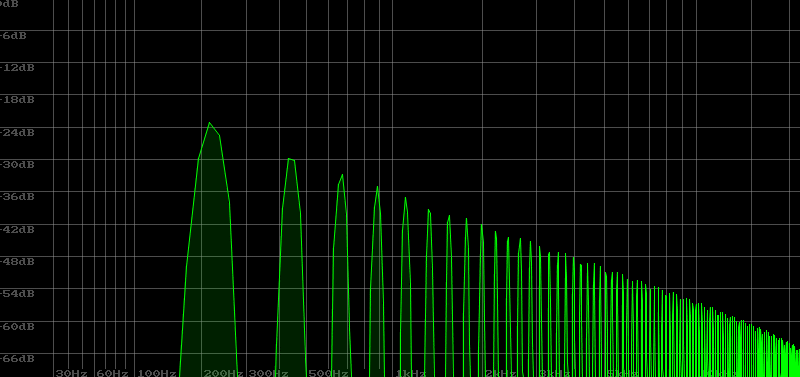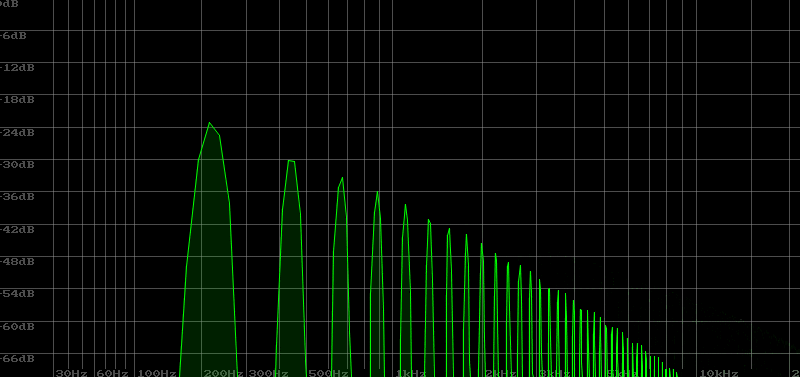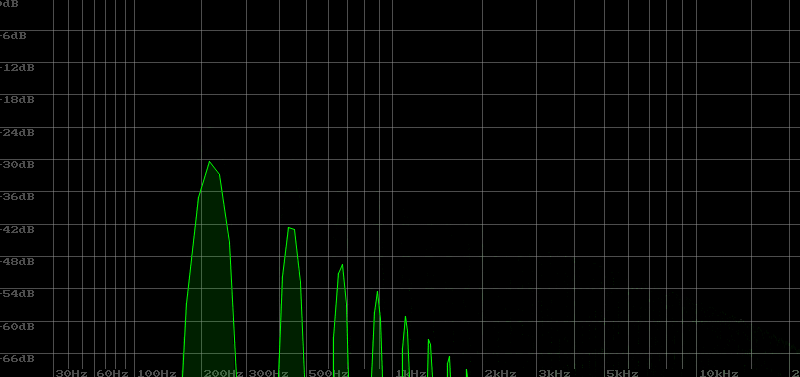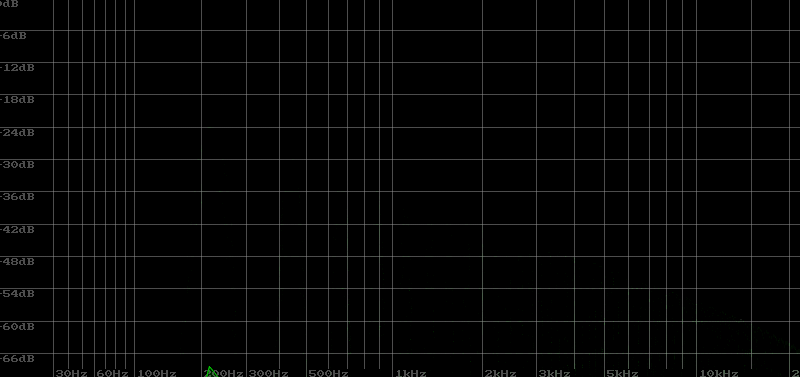
Filters included in Filterscape VA
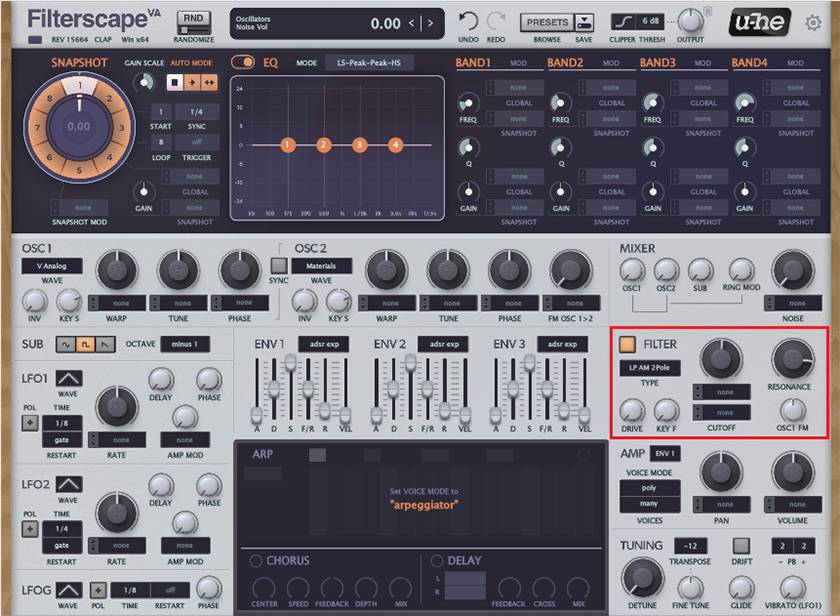
Since the name of the plug-in is Filterscape, a lot of effort is put into the filters. However, since the plugin has existed since 2005, some of the older filters have been retained to maintain compatibility. The new filters include a State Variable Filter, which handles LP low-pass, HP high-pass, and BP band-pass simultaneously in the same circuit. This is more useful in the Fileterscape effects plug-in than in the Fileterscape VA synth plug-in.
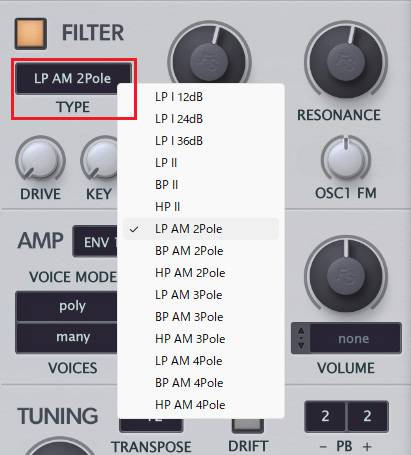
| FILTER | note |
|---|---|
| LP I 12dB | old Due to textbook signal processing, problems are likely to occur when rapid modulation is applied. |
| LP I 24dB | |
| LP I 36dB | |
| LP II | old The unique 2Pole filter allows you to create unique sounds. u-he free synth Podolski adopted filters. |
| BP II | |
| HP II | |
| LP AM 2Pole | State Variable Filter(State variable type filter) Self-oscillating As the number of poles increases, the effect becomes sharper. |
| BP AM 2Pole | |
| HP AM 2Pole | |
| LP AM 3Pole | |
| BP AM 3Pole | |
| HP AM 3Pole | |
| LP AM 4Pole | |
| BP AM 4Pole | |
| HP AM 4Pole |
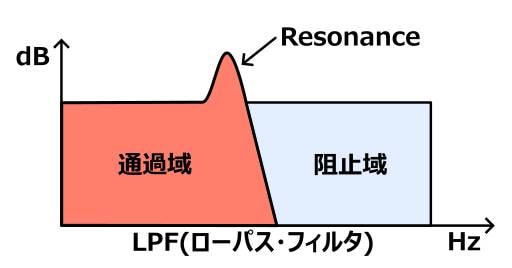
Resonance
In the case of synths, simply shaving them down with an ideal filter tends to result in a boring sound with just the high-frequency components shaved off. Therefore, it has become standard practice to use Resonance to give the sound a habitual character. When the Resonance is increased, the amplitude around the cutoff frequency becomes larger, and the sound becomes more pleasing to the ear. In the case of AM, if the Resonance is turned up too high, the filter itself will oscillate and sound sharp, so it is usually recommended to set the Resonance within the range where it doesn’t oscillate.
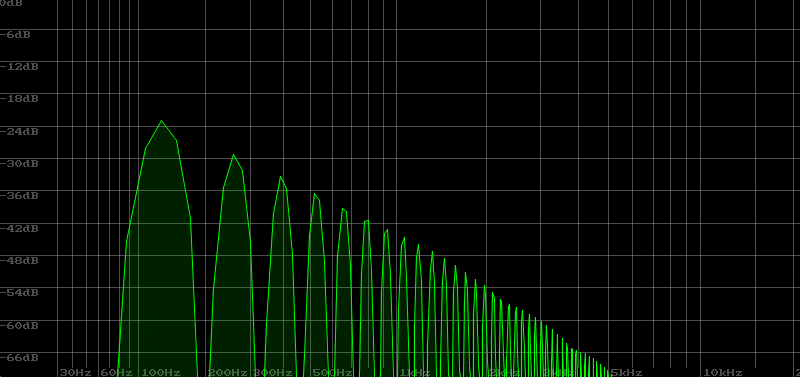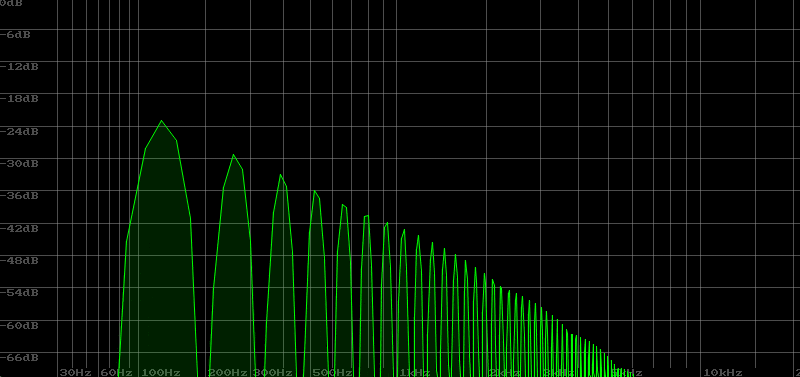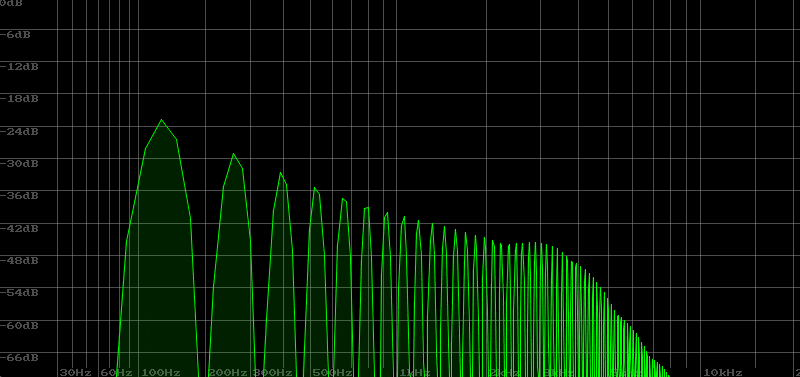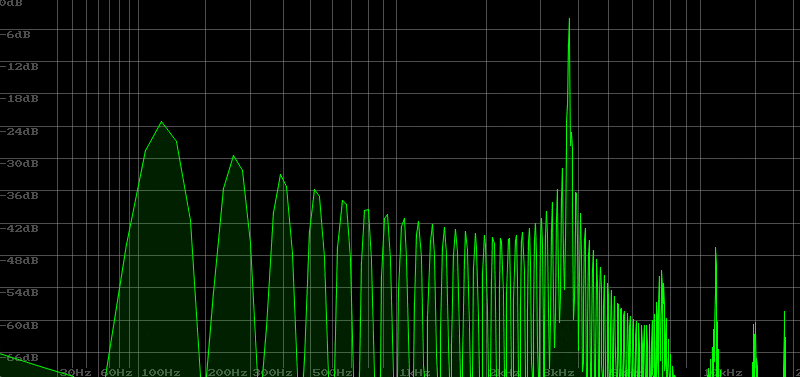
The following sample is the sound when Resonance is gradually increased from 0 to 100. The sound is heard as a squeal in the middle. This is called oscillation.
In the video, you can see the cutoff frequency rising as shown below. When it reaches a prominent peak, it is in a state of oscillation.
LPF Sound Samples
Below are some samples using LPF.
Standard resonance sound using LP AM 2Pole
The cutoff frequency of the LP AM 2Pole filter is lowered by the Envelope at the timing of note on for sawtooth waves that create a characteristic synth sound through resonance. The filter settings are as follows.

Distinctive Sound with LP II
With the following settings, you can create sounds that are difficult to achieve with other synths that have a sharp attack. Note that the attack will jump out of 0 dB without a hitch, so a limiter or another countermeasure is necessary.

Sound Created by Filter Self-Oscillation
The State Variable Filter allows for self-oscillation, making it possible to create a whistling sound without the need for an oscillator. However, the response speed slows down, so it can only be used for slow melodies. Setting KEY F to 100 makes it easier to get a sense of pitch.

HPF Sound Samples
In sound creation, LPF is often used, but sometimes you may want to use HPF. The video below shows a sawtooth wave with HPF applied. Since the sound is cut off from the base note, it becomes difficult to maintain the sense of pitch. So you can imagine that its use is limited.
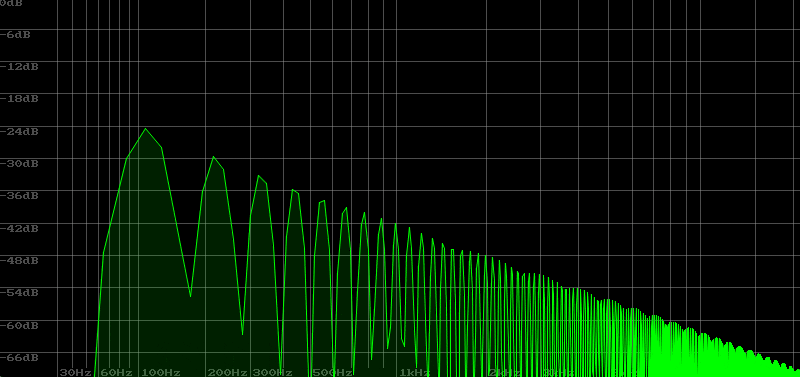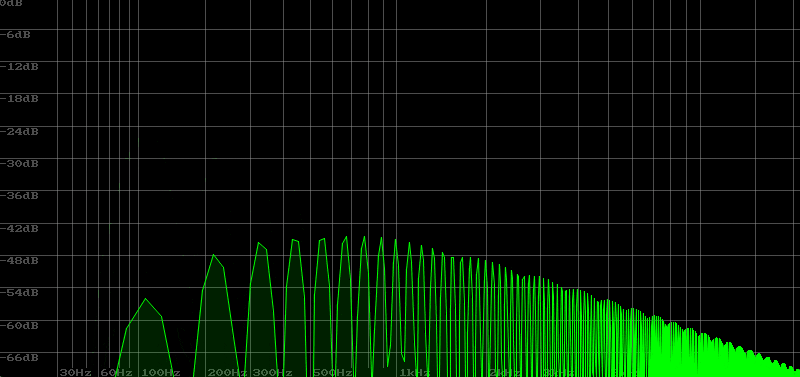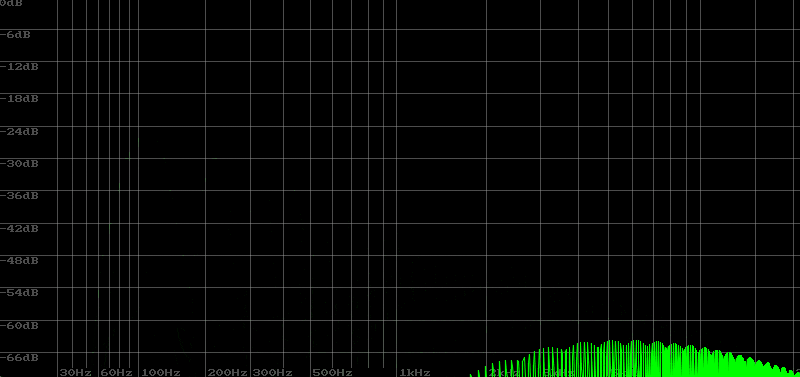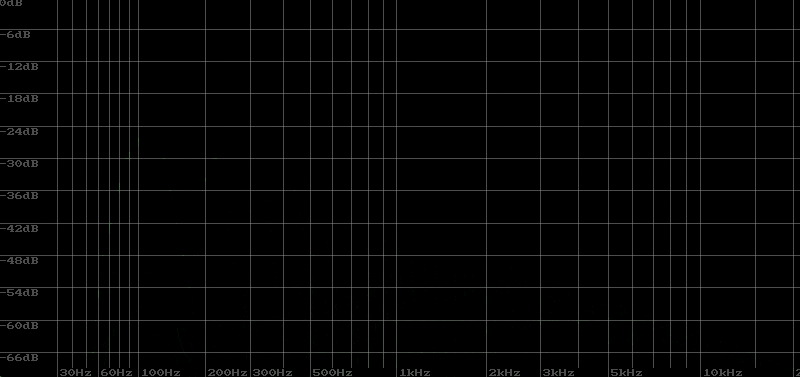
I tried to create a metallic sound, aiming for a sparkling sound by diluting the sense of pitch with HPF.
In the next issue, I will explain PWM, Sync, and things of this nature., which can be considered synth classics.
The “sound & person” column is made possible by your contributions.
For more information about submissions, click here.










![Exploring the Sounds of Analog Lab V, Part 1 [ARP 2600, B-3, Buchla Easel, Clavinet, CMI]](/contents/uploads/thumbs/5/2024/10/20241022_5_29062_1.jpg)



 定番DAWソフトウェア CUBASE
定番DAWソフトウェア CUBASE
 Native Instruments KOMPLETE 特集
Native Instruments KOMPLETE 特集
 WAVES バンドル・アドバイザー
WAVES バンドル・アドバイザー
 Steinberg 特集
Steinberg 特集
 ANTELOPE AUDIO 特集
ANTELOPE AUDIO 特集
 DTMセール情報まとめ
DTMセール情報まとめ














