This time, I’m going to talk about some potentially useful trivia about power supplies.
目次
- Trivia 1: What are AC and DC, and what do the symbols on a multimeter mean?
- Trivia 2: Are there differences in power supplies around the world?
- Trivia 3: What’s the difference between 3-prong and 2-prong power outlets?
- Trivia 4: What is a noise filter on a power strip?
Trivia 1
What are AC and DC, and what do the symbols on a multimeter mean?
When we talk about power supplies, we often mention AC and DC.
- AC(Alternating Current)
- = alternating current of electrical signal
- DC(Direct Current)
- = direct current of electrical signal
These are what they mean.
In everyday life, alternating current comes from wall outlets, while direct current is output from DC adapters. By inputting each type of output into an oscilloscope, you can visually understand the electrical signal waveform better.
AC (Alternating Current)
The horizontal axis center is 0V and an AC signal alternates between positive and negative regions vertically. A common household outlet outputs a sine wave, which is a smooth, repetitive oscillation. Other waveforms, such as triangular and square waves, also exist.
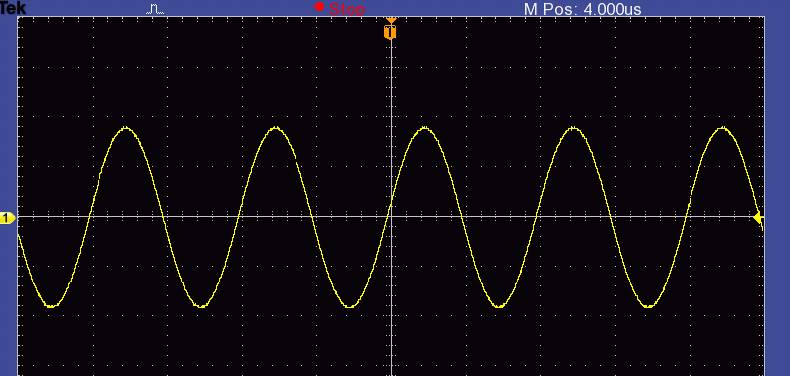
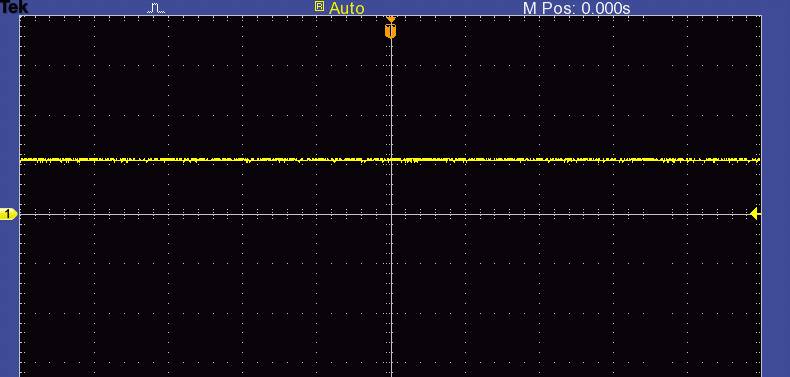
DC (Direct Current)
A DC signal is always either positive or negative, represented as a straight line in one of these regions.
The symbols for measurement modes on a multimeter are derived from the above reasons. Can you tell which one is for AC measurement and which one is for DC measurement?

Trivia 2
Are there differences in power supplies around the world?
Yes, there are differences. You might wonder why there isn’t a single global standard, but considering historical backgrounds, inter-nation issues, and infrastructure development processes, it has become quite complex globally.
Commonly, Europe, the US, and Japan have different standards.
Roughly speaking, Europe uses 230V, the US 120V, and Japan 100V.
Recently, many devices use universal power supplies that cover 100V-240V. Manufacturers often equip their globally marketed products with such power supplies.
For more details, refer to the following:
お役立情報 Keisoku Giken Cor. Ltd. - World Power Supply Voltages and Frequencies
Trivia 3
What’s the difference between 3-prong and 2-prong power outlets?


There are 3-prong (three-hole) and 2-prong (two-hole) power outlets. The third hole is for connecting the ground pin. In typical households, the power outlets for air conditioners, microwaves, and washing machines are either the 3-hole type or have a connection for an earth lug.
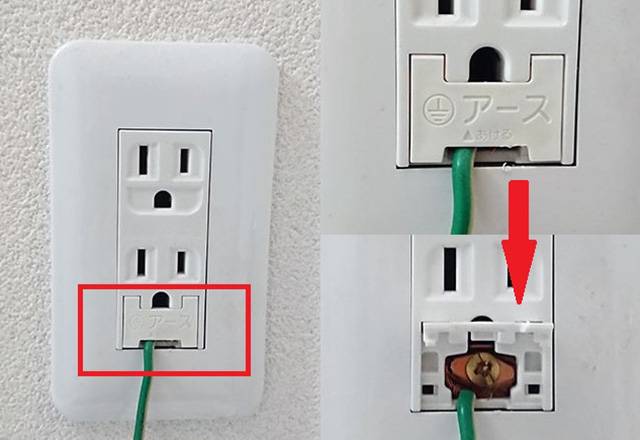
The purposes of grounding are as follows:
- To prevent electric shock
- In areas with moisture or humidity, the risk of electric shock increases. Grounding prevents such risks.
- To prevent lightning and short-circuit accident
- Grounding protects against accidents like fires by directing large currents from lightning or short circuits to the ground.
- To reduce external radiated noise
- Electronic devices around us emit noise, and grounding the metal casing of such devices can shield against incoming radiated noise, absorbing it into the ground and thus improving performance.
Trivia 4
What is a noise filter on a power strip?
You might think that a noise filter on a power strip simply cuts audible noise when you plug into it, but that is not actually the case.
Let’s use a detailed example.
CLASSIC PRO / Power Strip PDS8 3m
The noise filter performance of this product is as follows.
■Noise Attenuation: Transverse > 26dB, 200kHz-10MHz
Transverse refers to: a transverse wave≒electromagnetic wave.

“>26dB” indicates the amount of noise reduction.
“200kHz-10MHz” is the frequency range of the noise.
In other words, it attenuates electromagnetic noise (200kHz-10MHz) to below 26dB.
This frequency range is not within the audible range, so it doesn’t directly cut audible noise. Instead, it reduces high-frequency noise that can affect your device’s circuits and power supply, thereby reducing the cause of audio noise.
That’s all for today’s trivias!



















 電源アダプター特集
電源アダプター特集
 CLASSIC PRO 簡易PAシステム特集
CLASSIC PRO 簡易PAシステム特集
 簡易PAシステム タイプ別おすすめランキング
簡易PAシステム タイプ別おすすめランキング
 CLASSIC PRO パワーディストリビューター特集
CLASSIC PRO パワーディストリビューター特集
 停電時にパソコン、作曲データを守る!!
停電時にパソコン、作曲データを守る!!
 簡易PAセットとは
簡易PAセットとは














