Recently, It’s been freezing cold.
Whenever we receive repair requests for halogen lamps during this time of year, we always look forward to taking these cases on for some reason (No, it’s not because we just want to stay warm by the halogen lamps while we work. Absolutely not.)
Joking aside, I would like to start with the question: “What is a halogen lamp?”
Contents
- What is a halogen lamp?
- Structure of Halogen Light Bulbs
- The Benefits of Halogen Light Bulbs
- Trivia - Halogen Cycle
- Conclusion
■ What is a halogen lamp?
In a nutshell, a halogen lamp is a type of light bulb. You may have seen one in a shopping mall or on the street.
Both a “halogen lamp” and a “halogen light bulb” refer to the same thing.
You may be thinking, “A halogen lamp and an incandescent light bulb are the same thing, aren’t they?” but in fact, they’re slightly different. I’m going to compare how these two types of light bulbs are different.
(In order to compare with incandescent light bulbs, I’m going to use the term ‘halogen bulbs’ hereafter for consistency.)
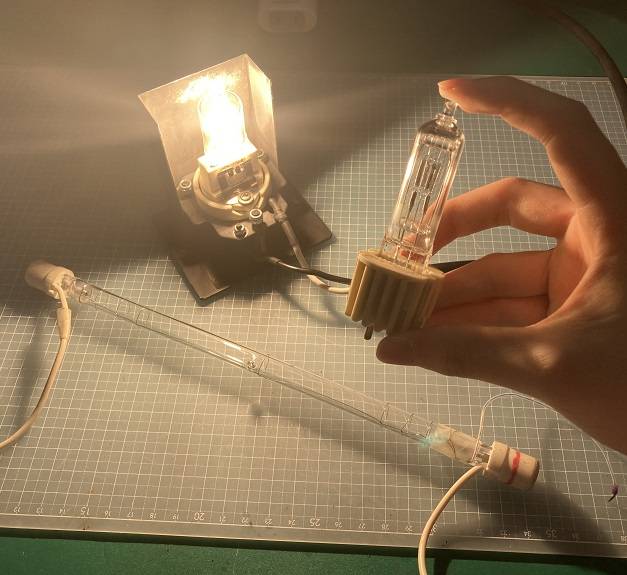
In terms of features, halogen light bulbs are smaller in size, brighter, and become considerably hotter than incandescent light bulbs.
They are usually used for spot lights and they are also used in stage lighting because the light they emanate is so strong. Furthermore, the brightness and color temperature rarely change while the light is connected and turned on to the power supply.
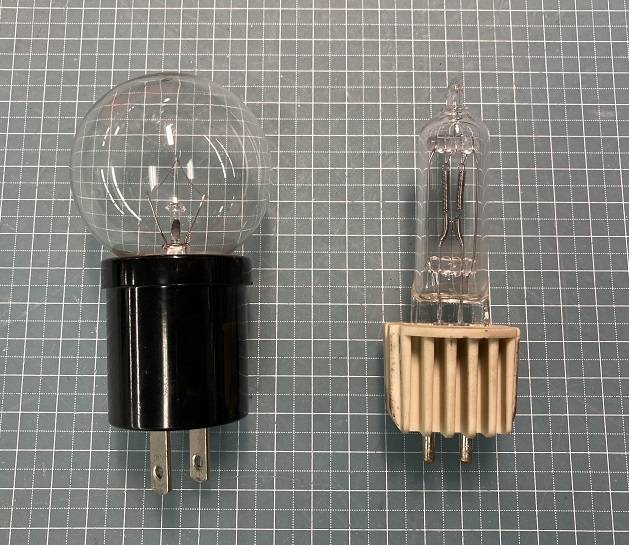

An Incandescent light bulb (Left) and a halogen light bulb (Right)
■ Structure of Halogen Light Bulbs
The filament (a thin metal wire) enclosed in the glass bulb is electrified to emit light. The inside of the glass bulb is filled with halogen gas, which is why it is called a halogen light bulb.
(By the way, incandescent light bulbs are filled with gasses like argon.)
■ The Benefits of Halogen Light Bulbs
Halogen light bulbs are able to emit strong light for their small size, so this makes the size of halogen lighting equipment more compact. Smaller size equipment reduces the cost for installation but still packs a lot of power.
Characteristics of halogen bulbs are stable in brightness and color temperature make it perfect lighting for store displays in commercial facilities and for the usage as a spotlight in studios and theaters.
■ Trivia - Halogen Cycle
Halogen light bulbs have a certain function.
When a halogen light bulb emits light, the filament in the center produces radiation and then becomes so hot that it evaporates. While this process is going on, the evaporated filament tungsten material chemically unites with halogen gas inside the tube. The tungsten material of the filament then becomes gas and is heated to return back onto the filament again.
This cycle prevents the filament from deteriorating as it becomes thinner, making it usable for a longer period of time. Specifically, they last about 2.5 times longer than regular incandescent light bulbs.
■ Conclusion
How was it? Halogen light bulbs become very hot and have a high output of power, so they seem to have a short lifespan.
However, halogen light bulbs have become indispensable in our daily lives because they actually have a surprisingly longer lifespan than incandescent light bulbs.
An example of where halogen light bulbs are seen everyday are usually the headlights of automobiles.
However, in recent years, more and more countries are phasing out the use of high-energy halogen light bulbs from an eco-friendly point of view. For example, in the UK, high-energy light bulbs are illegal to sell besides the ones that are especially designed for studio and stage lighting.
A number of Japanese manufacturers are also discontinuing the production of halogen light bulbs, and they have instead been encouraged to replace them with LED lights. However, halogen light bulbs will still be in demand for stage lighting, so I hope they don’t completely disappear.
Thank you so much for reading.
















![[2023 Edition] Recommended Lighting for Photography](/contents/uploads/thumbs/2/2022/6/20220602_2_18157_1.jpg)


 STAGE EVOLUTION ステージ照明
STAGE EVOLUTION ステージ照明
 AMERICAN DJ ステージ照明
AMERICAN DJ ステージ照明
 ステージ照明の調光器
ステージ照明の調光器
 プロ仕様 ステージ照明 ELATION
プロ仕様 ステージ照明 ELATION
 小さなパーティでも役立つカッコイイ照明機材
小さなパーティでも役立つカッコイイ照明機材
 照明入門講座
照明入門講座















