This is another explanation of the PCM method, this time concerning the wavetable method, which uses sampled (recorded) sound but also actively processes it to create sound. Wavetable is not a method of playing back recorded data from beginning to end, as is the case with sampled sound sources. Basically, the sound is created by looping one cycle of waveforms, so it is a sound source that can be used with a small amount of memory. Since repeating a single waveform alone is not expressive enough, various effects were obtained by smoothly switching multiple waveforms on the time axis. The wavetable shown below has only three waveforms, but the waveforms change smoothly as shown in the video. The length of the sound is also flexible. If this were a PCM (Pulse Code Modulation), only three waveforms can produce a sound with an indistinct pitch.


Wavetables have consequently opened up new possibilities for digital synthesizer size rather than realistic sound reproduction. In today's world of ample memory, the appeal of these methods is not so much the memory savings as it is the unique sound variations.
The term “wavetable” seems to have a somewhat diverse interpretation, and opinions differ from person to person. Here, we will talk about it roughly as a synth that actively utilizes digital waveforms for a single cycle.
PCM WAVETABLE
From the late 1970s to the 1980s, memory was extremely expensive, which was the catalyst in the creation of inexpensive digital instruments. Therefore, digital sound sources that could make do with less memory were being researched and developed, and PPG WAVE was one of the first to appear on the market.
1982 PPG WAVE 2.2 Germany, about 2 million yenPPG
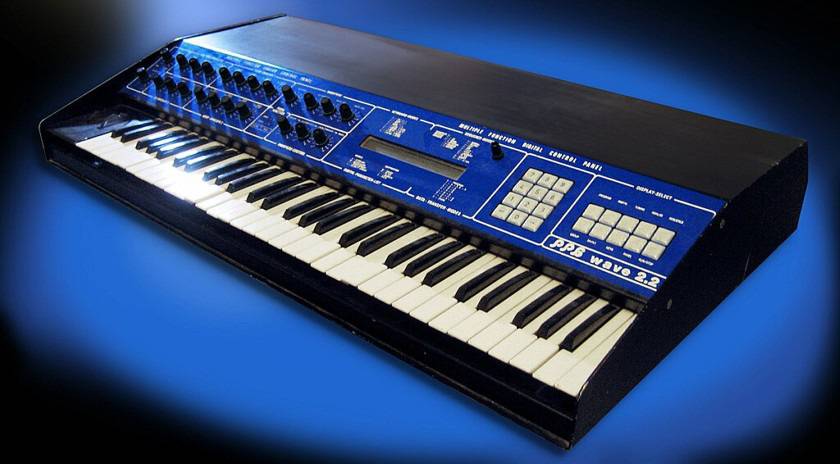

PPG WAVE 2.2, CC BY-SA 2.0 (cited from Wikipedia)
Although the internal specifications of PPG are a mystery, it is likely that each wavetable had a set of 256 waveforms for one cycle, which were then called and generated. The number of samples per wavetable is small, probably less than 128 samples. The number of bits is also small, ranging from 8 to 12 bits. The figure below shows a part of the wavetable.

Each voice had two oscillators, and it was possible to play eight chords. The PPG was used frequently in popular music in the 1980s even though its production numbers were small. It had a distinctive digital sound that was different from the analog synths and acoustics that had been used up to that time, and it was very impressive.
PCM+Alpha Hybrid Sound Source
In the 80's, companies were making various efforts to save on memory. In 1983, Yamaha released the DX7, a fully digital FM synthesizer, and its explosive sales led to a flurry of digital synthesizers from various companies. Roland and Korg are the only two that are featured here, and I think it can be said that both of these sound sources are based on a concept similar to that of a wavetable. They also combined analog circuitry, making them hybrid digital/analog sound sources.
1984 KORG DW-6000 List Price ¥184,000

KORG's first digital synthesizer, the DW-6000's D.W.G.S. sound source digitally simulates the characteristics of acoustic instruments by preparing eight types of waveforms that are synthesized by adding harmonics instead of recorded PCM. The sound source is not a recorded PCM. Therefore, the sound source is not a recorded wavetable, but the concept is similar, so I would like to treat them as such. The synthesized sounds are brass, violin, piano, electric piano, bass, saxophone, clavi, bells and acoustic instruments as shown in the figure below. The overtone composition is also written. The reason why they synthesized them first was because the computation speed was too slow for real-time processing. In order to reduce the computation cost, it was necessary to synthesize the sound in advance. The sound creation was analog filters and amplifiers, so it could be handled in a manner similar to conventional analog synthesizers.
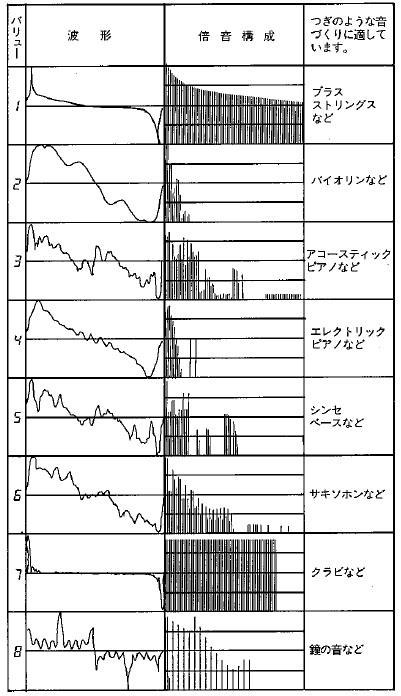
Figure: Chart from the manual
1987 Roland D-50 List Price ¥238,000

The LA sound source in the D-50 is Roland's original sound source inspired by Yamaha's FM sound source. By using characteristic sampling for the attack and combining basic waveforms in the loop section and processing them with an analog filter, a distinctive sound that is neither an analog synth nor an FM sound source was created. It can be said to be a sound source that uses a small amount of memory efficiently. This model was accepted and widely used worldwide and contains sounds that can still be heard today.
After Wavetable synthesizers
PCM synthesizers began to take the lead at the end of the 1980s as memory became cheaper. As a result, wavetable synthesizers were no longer seen in the market. Since then, it has been the golden age of PCM synthesizers up to the present day. Even though new types of synthesizers have emerged from time to time, they have not been able to threaten the PCM synthesizers. However, PCM synthesizers have been extended in various ways and developed in such a way that they are internally fused with other synthesizers, making it difficult to categorize them by sound source.
Software Sound Sources
On the other hand, software synthesizers began to be developed in earnest after 2000, and wavetables were making a comeback. In the past decade, they have gained even more momentum and have become a central part of EDM systems. In fact, its increased memory capacity and processing speed have made it into a versatile synth that can also be handled in a sampling fashion.
Xfer Records SERUM 20,000-30,000 yenQuoting

From the Xfer Records website,
I think the current representative soft synth is the Xfer Records SERUM. It has an excellent interface that is easy to understand visually. The 3D waveform display is reminiscent of Fairlight C.M.I. The number of waveform samples per cycle is 2048, and the set contains 256 of them, so it is possible to reproduce raw sounds. However, it is different from the sampling method in that it aims to create a unique sound rather than a reproducible sound. Morphing, which smoothly changes from one waveform to another, is an important element, and it seems to actively create unique changes that cannot be obtained with physical instruments. The waveforms provided are also noticeably more geometric than the raw samples.
vital audio VITALIntroducing
Another soft synth. This one has a free version, so feel free to use it. As you can see, it is a wavetable type synthesizer that is designed with SERUM in mind. Wavetable data is compatible with SERUM, so you can use it as well. Although the load is high, I think it is easy to use.
The Future of Wavetables
The hardware wavetable synths of the 80s were short-lived, but the current software wavetable synths have expanded their possibilities and have gained support as versatile synths that can cover everything from analog sounds to sampled instruments. And, the internal fusion with other sound sources has made it necessary to use the ambiguous term "wavetable-based sound source”. It seems that the era of classifying by sound source type is coming to an end.
The “sound & person” column is made up of contributions from you.
For details about contributing, click here.















 定番DAWソフトウェア CUBASE
定番DAWソフトウェア CUBASE
 iZotopeが手がけるオールインワンDAW “Spire”
iZotopeが手がけるオールインワンDAW “Spire”
 DTMセール情報まとめ
DTMセール情報まとめ
 USB接続MIDIインターフェイス
USB接続MIDIインターフェイス
 USB接続対応のMIDIキーボード
USB接続対応のMIDIキーボード
 DTMに必要な機材
DTMに必要な機材














